Clang structure
It originated from the "Silk Road" that was directly introduced to Xinjiang, which should have been earlier than the end of the Ming Dynasty, and then spread to Hami, eastern Xinjiang at the end of the 18th century.
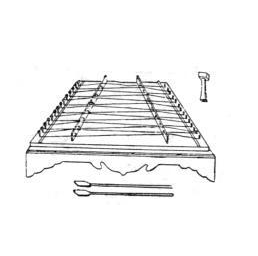
The shape is the same as that of the inland dulcimer, consisting of a resonance box, a mountain pass, a peg, a bridge pin, a bridge, a string and a bamboo.
sound box
It is in the shape of a flat trapezoid. It is formed by gluing the frame, the surface and the bottom plate. The frame is composed of the front and rear side panels and the headstock at the left and right ends. The frame panels are mostly made of colored wood, birch, elm or other hard miscellaneous woods. The right headstock where the pegs are installed is mostly made of multi-layer colored wood (with staggered grains) plywood. The top of the piano frame is covered with fish scale spruce, paulownia or pine veneer, and the bottom plate is mostly made of three-layer plywood. There are two round sound holes on the top or bottom plate.
Yamaguchi
The long wooden strips on both sides of the panel are made of mahogany. The length of the string from the mountain pass to the horse peak is the effective string length for the vibration of the strings.
peg
Special metal screws, rounded at the top and bottom, are used for string winding and tuning.
pegs
Made of metal, it is mounted on the left headstock for tying the strings.
bridge
Straight strip, peak and valley shape, made of mahogany, bamboo or horn, one to five, placed on the panel, the left side is the treble and alto horse, the right side is the bass horse, the horse peak is used for stringing, the horse Valley for another horse string to pass through.
strings
Copper wire strings are mostly used, and bare strings are used for the middle and high pitches. Each tone is a group of three strings. No. 27 to No. 31 steel wires are commonly used; sound.
Qin Bamboo
Also known as qin chuan, it is made of bamboo, with two pieces a pair, shorter and harder than the inland ones, generally 24 cm long.
 渝公网安备 50010702504639号
渝公网安备 50010702504639号